Laravel 8 One To Many Polymorphic Relationship
Websolutionstuff | Nov-19-2021 | Categories : Laravel PHP MySQL
In this tutorial we will learn about laravel 8 one to many polymorphic relationship. A one-to-many polymorphic relation is similar to a typical one-to-many relation. the child model can belong to more than one type of model using a single association. One to many polymorphic relationship used when a model belongs to more than one other model on a single association model.
For Example, users of your application can comment on posts and videos. Using polymorphic relationships, you may use a single comments table to contain comments for both posts and videos. using morphMany() and morphTo() you can access data.
In this example we will create posts, comments and videos table. all tables are connected with each other like below screenshot and we are create migration and model all table and retrive data using one to many polymorphic relationship in laravel 6, laravel 7, laravel 8.
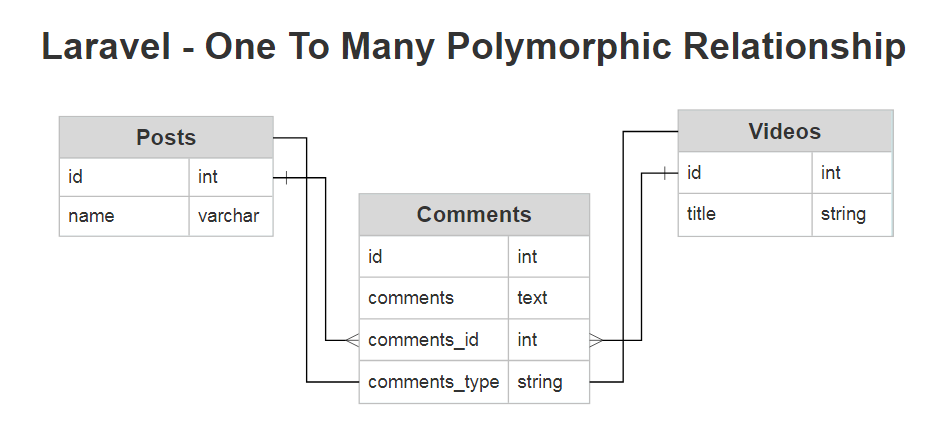
Now, we will create migration for posts, comments and videos table. and add foreign key in posts and videos table.
Post Table :
Schema::create('posts', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("name");
$table->timestamps();
});
Comment Table :
Schema::create('comments', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->text("comments");
$table->integer('commentable_id');
$table->string("commentable_type");
$table->timestamps();
});
Video Table :
Schema::create('videos', function (Blueprint $table) {
$table->increments('id');
$table->string("title");
$table->timestamps();
});
Now, we will create Post, Comment and Video model.
Post Model :
class Post extends Model
{
/**
* Get all of the post's comments.
*/
public function comments()
{
return $this->morphMany(Comment::class, 'commentable');
}
}
Comment Model :
class Comment extends Model
{
/**
* Get the parent commentable model (post or video).
*/
public function commentable()
{
return $this->morphTo();
}
}
Video Model :
class Video extends Model
{
/**
* Get all of the video's comments.
*/
public function comments()
{
return $this->morphMany(Comment::class, 'commentable');
}
}
Once your database table and models are defined, you may access the relationships via your model's dynamic relationship properties. For example, to access all of the comments for a post, we can use the comments property.
$post = Post::find(1);
foreach ($post->comments as $comment) {
//
}
You may also retrieve the parent of a polymorphic child model by accessing the name of the method like below code.
$comment = Comment::find(1);
$commentable = $comment->commentable;
Now, we will give you example of create record for one to many polymorphic relationship like below code.
$post = Post::find(1);
$comment = new Comment;
$comment->comments = "this is test comments from websolutionstuff";
$post->comments()->save($comment);
You might also like :
- Read Also : Laravel 8 CRUD Operation Example
- Read Also : Bootstrap Daterangepicker Example
- Read Also : Google Recaptcha Example In Laravel
- Read Also : How To Create Dark and Light Mode Website using jQuery
Recommended Post
Featured Post
How To Change Month Name In jQ...
In this article, we will see how to change the month name in jquery datepicker. In the date picker, we can change t...
Jul-01-2022

How to Add Image to PDF file i...
Greetings, Laravel enthusiasts! Today, let's explore a practical aspect of web development – adding images to...
Dec-20-2023

Carbon Add Months To Date In L...
In this article, we will see an example of carbon add months to date in laravel. Here, we will give you a simple&nb...
Dec-05-2020

How To Get Client IP Address I...
In this article, we will see how to get a client's IP address in laravel 9. Many times you need a user IP addre...
Oct-26-2022